
Zn ( d ) = Re ( zn ) + j Im ( zn ) = r + jx Let’s represent the reflection coefficient in terms of its coordinates The normalized impedance is represented on the Smith chart by using families of curves that identify the normalized resistance r (real part) and the normalized reactance x (imaginary part)
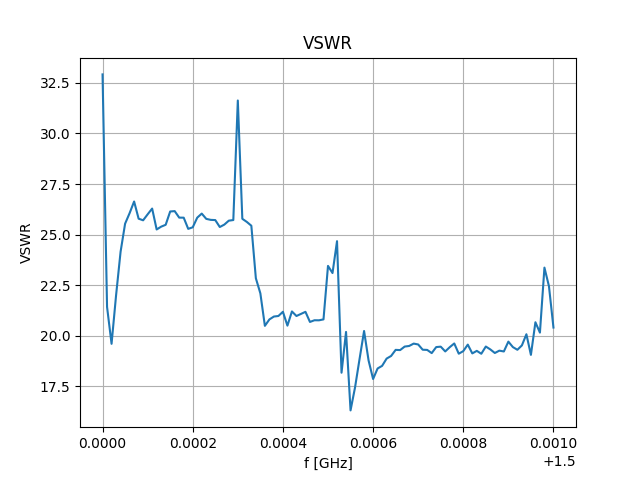
SMITH CHART VOLTAGE MINIMUM SERIES
Z (d ) 1+ Γ(d ) zn ( d ) = Z0 1− Γ(d ) © Amanogawa, 2006 - Digital Maestro Series In order to obtain universal curves, we introduce the concept of normalized impedance It is obvious that the result would be applicable only to lines with exactly characteristic impedance Z0. V(d) 1+ Γ(d) = Z0 Z( d ) = I(d) 1− Γ(d) This provides the complex function Z( d ) = f that we want to graph. To do so, we start from the general definition of line impedance (which is equally applicable to a load impedance when d=0) The goal of the Smith chart is to identify all possible impedances on the domain of existence of the reflection coefficient. © Amanogawa, 2006 - Digital Maestro Series In the case of a general lossy line, the reflection coefficient might have magnitude larger than one, due to the complex characteristic impedance, requiring and extended Smith chart. This is also the domain of the Smith chart. The domain of definition of the reflection coefficient for a loss-less line is a circle of unitary radius in the complex plane. From a mathematical point of view, the Smith chart is a 4-D representation of all possible complex impedances with respect to coordinates defined by the complex reflection coefficient. The chart provides a clever way to visualize complex functions and it continues to endure popularity, decades after its original conception. Smith Chart The Smith chart is one of the most useful graphical tools for high frequency circuit applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
